Applications
PRCISR™ CRISPR libraries in action
Applications enabled by PRCISRTM CRISPR libraries
Single targeting pooled libraries
- Knockout: drug sensitivity and resistance, context-dependency, reporter screens
- Inhibition or overexpression: cancer regulator mutations, target discovery
- Target validation: focused set of genes or families in various contexts, isogenic screens
- Others: Epigenetic regulation, chromatin purification, etc.
Fixed-pair pooled libraries
- Enhanced gene editing rates: when sgRNA pairs are used to knockout a single gene (e.g. dual exon targets, DNA excision))
- Validation of combinatorial hits: using this method reduces the scale by a targeted approach
- Gene or protein structure characterization: gene, exon or domain tiling
- Target non-coding genome: DNA excision (e.g. lncRNAs, miPs, smORFs)
- Variant screening: editing reporter systems, protein engineering, mutational scanning or saturation screens (mutate all possible / relevant positions of a gene)
- Also useful for barcoded libraries: track single cells or cell populations
Multiplex pooled libraries
- Combinatorial effects between gene families of interest: genetic interactions, synthetic lethality, paralog buffering (all by-all, few-by-all, etc.)
- Orthogonal combinatorial applications: disease modeling and vulnerability testing, functional buffering, target discovery, context-independent isogenic screens (e.g. knockout, inactivation, activation in one system)
Link to our proprietary PRCISRTM technology
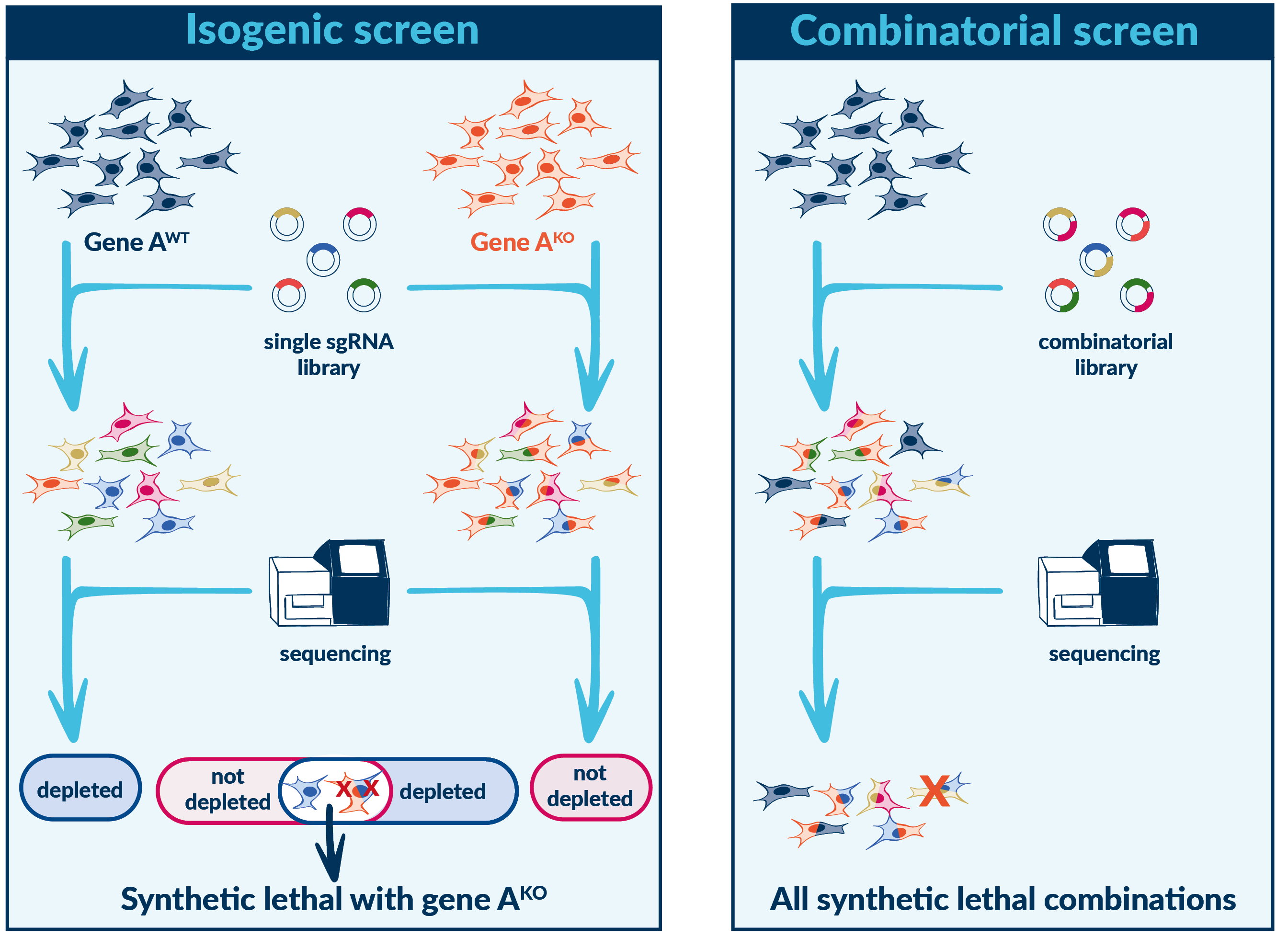
Synthetic lethality screening
Genetic interactions occur when the combination of two mutations lead to a phenotype that is more severe than either mutation alone. Synthetic lethality is an extreme example of a negative genetic interactions, in which the combination of mutations leads to cellular death.
Synthetic lethality exploits the genetic vulnerabilities of diseased cells by identifying combinations of genetic alterations, where the presence of one mutation sensitizes the diseased cell to the inhibition of another gene or pathway. When these vulnerabilities are targeted, diseased cells can be selectively killed while sparing healthy cells, leading to more effective.
PRCISR™ CRISPR libraries enable synthetic lethality screens that test all possible gene combinations in a single experiment, maximizing hit retention rates while minimizing false negatives, and allows experimental downscaling (up to 10-fold).
Case studies:
Few-by-all: Combinatorial screens uncover genetic interactions in autophagy.
Nucleic Acids Res. 2021; 49(10): 5684-5704. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkab309.
All-by-all: Combinatorial cells uncover metabolic rewiring in acute myeloid leukemia (AML)
Cancers (Basel). 2021; 13(23):6142. doi: 10.3390/cancers13236142.
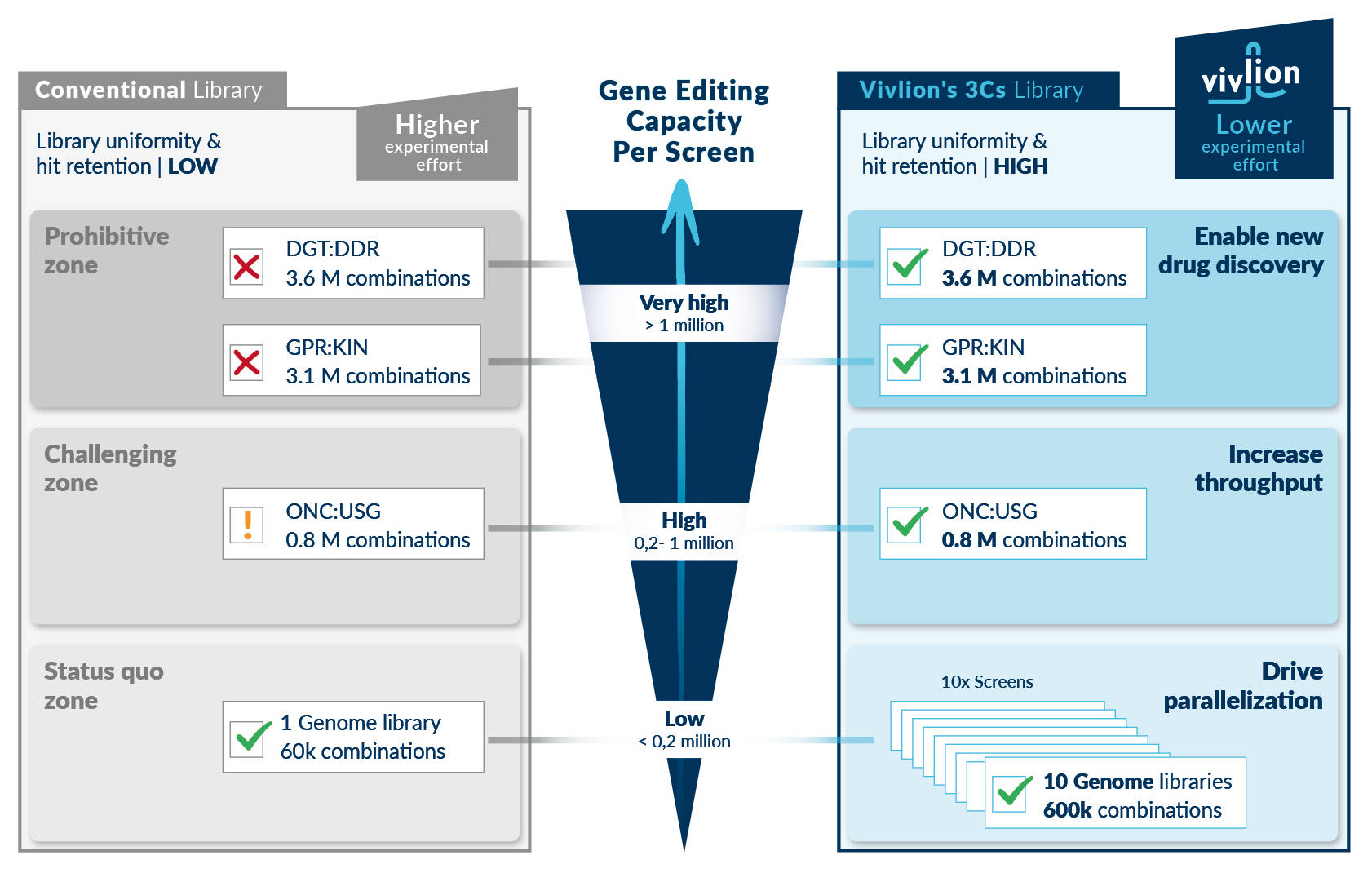
Parallel screening and experimental downscaling
Vivlion’s uniform PRCISR™ CRISPR libraries enable downscaling of experiments without impeding phenotypic separation or hit calling, thereby facilitating parallel screening in multiple contexts and treatments. In addition, these screens can be used for applications that are beyond the reach of conventional PCR libraries – e.g. target identification in more than 1 M genes etc.
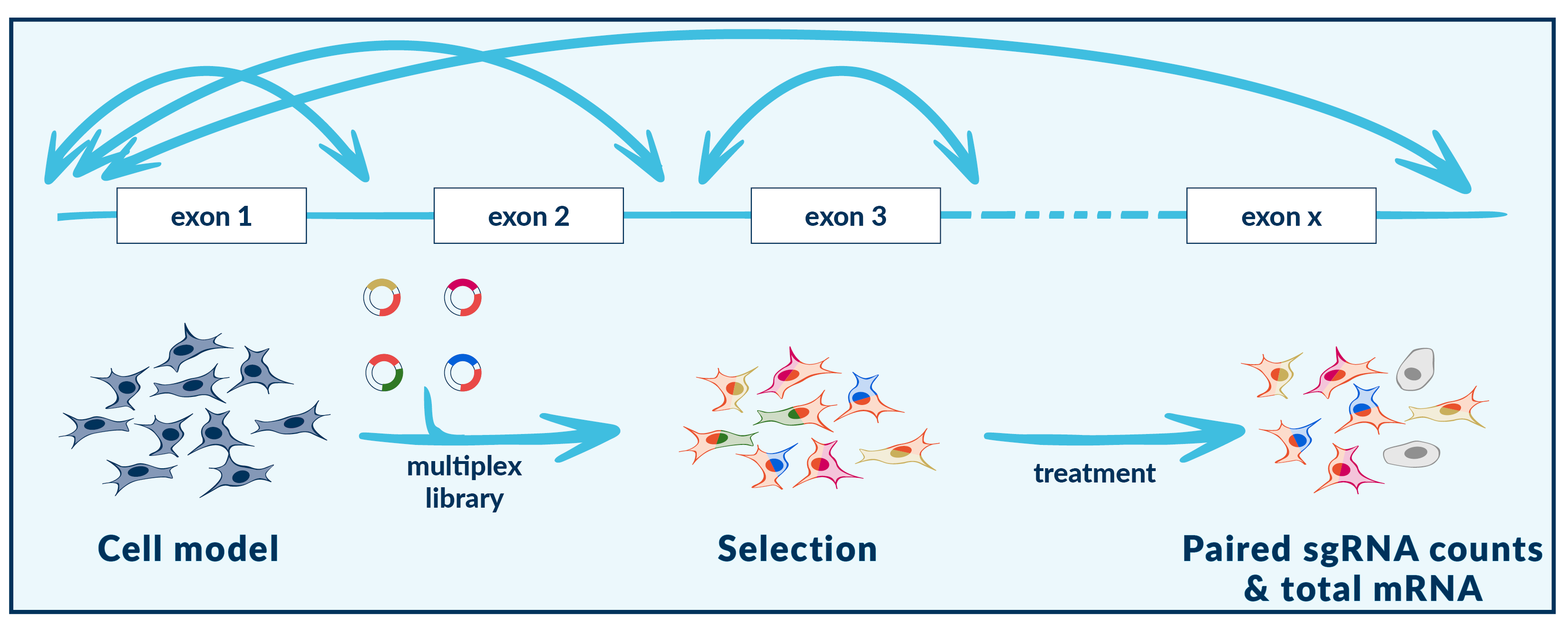
Multiplexing in DNA excision & exon tiling
Vivlion’s PRCISR™ CRISPR multiplex libraries enable DNA excision and domain tiling. When target sequences are in close proximity, the interspanning DNA is excised, enabling the unbiased investigation of coding and non-coding sequence elements. These libraries can be used to explore:
- gene-exon compositions
- tiling of cis-regulatory elements
- functional annotation of non-coding sequences
Contact us
We would like to hear more about your CRISPR questions and applications – please reach out to us by completing the following form: